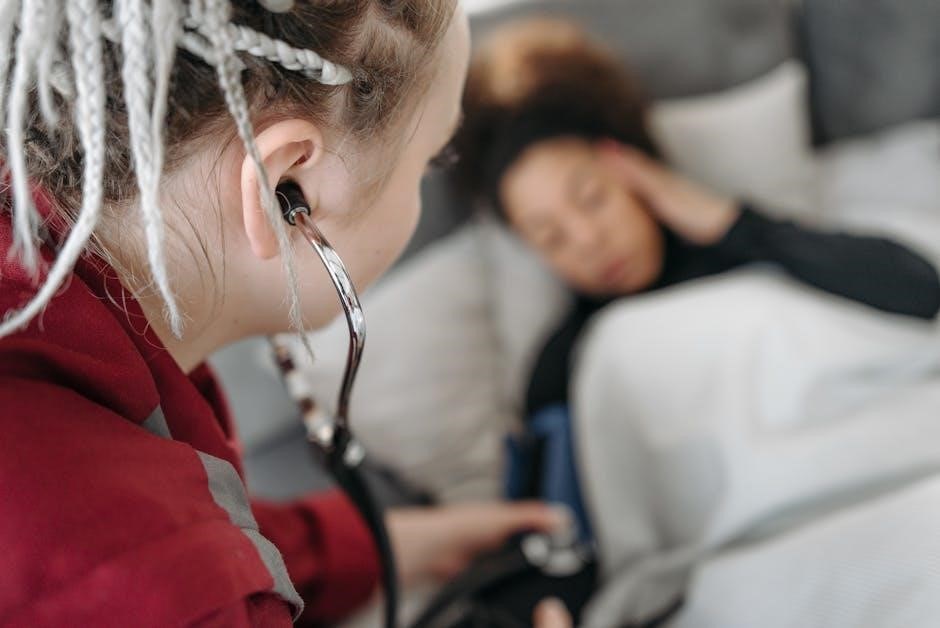
Nursing Assistant care involves providing essential support to patients, encompassing daily living activities and vital sign monitoring, as detailed in training handbooks.
What is a Nursing Assistant?
Nursing Assistants, often called Nurse Aides, are frontline healthcare professionals crucial to patient well-being. They provide direct care under the supervision of registered nurses (RNs) or licensed practical nurses (LPNs). Their role centers around assisting patients with activities of daily living – bathing, dressing, eating, and mobility.
A foundational understanding of Nursing Assistant duties is often gained through a NATCEP-approved training program, culminating in competency evaluation and registry listing. These programs, detailed in candidate handbooks, equip individuals with essential skills. They are vital members of the healthcare team, offering compassionate support and contributing significantly to the overall patient experience. Their work is regulated, ensuring quality care standards are met.
The Role of a Nursing Assistant in Healthcare
Nursing Assistants fulfill a vital role within the healthcare continuum, bridging the gap between patients and nursing staff. They observe and report changes in patient condition, contributing to informed care decisions. Responsibilities extend to maintaining a clean and safe environment, assisting with basic medical procedures, and providing emotional support.
Understanding patient rights and adhering to confidentiality protocols, as outlined in Nurse Aide registries and training handbooks, are paramount. They work in diverse settings – hospitals, nursing homes, and assisted living facilities – requiring adaptability and strong interpersonal skills. Their dedication directly impacts patient comfort and recovery, making them indispensable members of the healthcare team.

Basic Nursing Skills
Nursing Assistants require proficiency in fundamental skills, including vital sign measurement, personal hygiene assistance, and safe patient mobility techniques, per NATCEP standards.
Vital Signs Monitoring
Vital signs are crucial indicators of a patient’s physiological state, demanding accurate assessment by Nursing Assistants. This includes routinely taking temperature using various methods, carefully measuring pulse rate to detect irregularities, and diligently assessing respiration rate for signs of distress.
Furthermore, precise blood pressure measurement is essential for identifying potential cardiovascular issues. Proper technique and adherence to established protocols, as outlined in Nurse Aide training and candidate handbooks, are paramount. Consistent and detailed documentation of these vital signs allows healthcare professionals to effectively monitor patient conditions and implement appropriate interventions, ensuring optimal care and patient safety.
Taking Temperature
Taking temperature accurately is a fundamental skill for Nursing Assistants, utilizing oral, rectal, axillary, or tympanic routes. Understanding normal temperature ranges and variations is crucial, alongside recognizing factors influencing readings. Proper technique, including probe placement and ensuring patient comfort, is essential for reliable results.
Nurse Aide training emphasizes meticulous documentation of temperature readings, noting the method used and any relevant observations. Adherence to infection control protocols, like using disposable probe covers, prevents cross-contamination. As detailed in training handbooks, promptly reporting abnormal temperatures to the nurse facilitates timely intervention and patient care.

Measuring Pulse Rate
Measuring pulse rate involves assessing the number of heartbeats per minute, typically at the radial or apical site. Nursing Assistants learn to locate pulse points accurately and utilize a watch with a second hand for precise timing. Understanding normal pulse rate ranges, and recognizing factors influencing it – like activity or medication – is vital.
Consistent technique, including gentle palpation and avoiding excessive pressure, ensures accurate readings. Detailed documentation, noting the pulse rate, rhythm, and strength, is crucial. As outlined in Nurse Aide handbooks, promptly reporting any irregularities or significantly abnormal rates to the nurse is paramount for effective patient monitoring and care.
Assessing Respiration Rate
Assessing respiration rate requires observing the patient’s breathing pattern – the number of breaths taken per minute – without alerting them to avoid altering their natural rhythm. Nursing Assistants typically observe chest rise and fall, counting breaths for a full minute to ensure accuracy. Recognizing normal ranges and identifying factors influencing respiration, such as pain or anxiety, is essential.
Documenting the rate, depth, and character of respirations (e.g., shallow, labored, noisy) is vital. As detailed in Nurse Aide training materials and handbooks, promptly reporting any abnormalities – like shortness of breath or irregular breathing – to the supervising nurse is crucial for timely intervention and patient safety.
Blood Pressure Measurement
Blood pressure measurement, a core skill for Nursing Assistants, involves using a sphygmomanometer to determine systolic and diastolic pressures. Proper technique is paramount: ensuring the patient is seated comfortably, with their arm supported at heart level. Accurate cuff size selection is also critical for reliable readings, as outlined in Nurse Aide training handbooks.
Assistants record both systolic (pressure during heart contraction) and diastolic (pressure when the heart rests) values, noting any irregularities. Promptly reporting abnormal readings – high or low blood pressure – to the supervising nurse is essential for appropriate medical intervention and patient well-being, ensuring timely care and safety.
Personal Hygiene Assistance
Personal Hygiene Assistance is a fundamental aspect of Nursing Assistant care, promoting patient dignity and preventing infection. This encompasses assisting with bathing, oral care, and skin maintenance, all detailed within Nurse Aide training materials and handbooks. Assistants must prioritize patient privacy and comfort throughout these procedures, offering support while respecting independence.
Careful observation of skin condition is crucial, noting any redness, breakdown, or irritation. Proper techniques for bathing, including gentle washing and thorough drying, are essential. Maintaining oral hygiene prevents complications, and consistent skin care protects against pressure ulcers, contributing to overall patient well-being and quality of life.
Bathing Procedures
Bathing Procedures, as outlined in Nurse Aide training and handbooks, require a systematic approach prioritizing patient safety and comfort. Assistants must always explain the procedure, ensure privacy, and maintain a therapeutic environment. Water temperature should be carefully checked to prevent burns, and assistance provided based on the patient’s abilities.
Whether a bed bath, tub bath, or shower, gentle handling and thorough drying are vital. Observe the skin for any signs of breakdown or irritation during the bath. Encourage patient participation whenever possible, promoting independence and dignity. Proper documentation of any skin changes or concerns is also a crucial part of the process.
Oral Hygiene
Oral Hygiene is a fundamental aspect of patient care, detailed within Nurse Aide training materials and handbooks. Maintaining a clean mouth prevents infection and promotes overall well-being. Assistants should gather supplies, explain the procedure, and ensure patient comfort throughout. Gentle brushing and flossing, or rinsing if unable to perform these tasks, are essential.
Observe the mouth for sores, bleeding, or any abnormalities, reporting findings to the nurse. Proper positioning is crucial, especially for patients with swallowing difficulties. Encourage independence where possible, assisting only as needed. Regular oral care contributes significantly to a patient’s dignity and quality of life.
Skin Care and Prevention of Breakdowns
Skin Care is paramount in preventing pressure ulcers and maintaining patient comfort, as emphasized in Nurse Aide handbooks. Frequent repositioning, at least every two hours, is vital to relieve pressure. Keep skin clean and dry, using mild soaps and patting—not rubbing—the skin. Moisturize dry areas to prevent cracking.
Inspect skin daily for redness, blisters, or open areas, promptly reporting any concerns. Utilize protective barriers like creams or dressings where needed. Ensure bed linens are clean, dry, and wrinkle-free. Proper nutrition and hydration also contribute to skin health. Consistent, diligent skin care significantly reduces the risk of skin breakdown.
Mobility and Positioning
Mobility and proper positioning are crucial for preventing complications like pressure ulcers and contractures, as detailed in Nurse Aide training materials. Nursing Assistants assist patients with ambulation, ensuring a safe environment free of obstacles. Safe patient transfers require utilizing proper body mechanics – bending knees, keeping the back straight, and pivoting.
Regular repositioning, typically every two hours, is essential. Utilize pillows and supports to maintain proper alignment and comfort. Encourage patients to participate in range-of-motion exercises when possible. Always communicate with the patient before moving or repositioning them, explaining the process and ensuring their cooperation.
Assisting with Ambulation
Assisting with ambulation requires careful observation and support from the Nursing Assistant. Before assisting, ensure the patient is wearing appropriate footwear – non-skid socks or shoes. Assess the patient’s strength and balance, and provide assistance based on their individual needs. Utilize assistive devices like walkers or canes if prescribed, ensuring they are properly adjusted.
Walk at the patient’s pace, offering support at their weaker side. Encourage the patient to take small, steady steps. Be prepared to provide assistance if the patient feels unsteady or dizzy. Always communicate clearly and reassure the patient throughout the process, promoting confidence and independence.
Transferring Patients Safely
Transferring patients safely is paramount for both the patient’s well-being and the Nursing Assistant’s safety; Prior to any transfer, explain the procedure clearly to the patient, ensuring their understanding and cooperation. Assess the patient’s physical capabilities and any limitations. Utilize proper body mechanics – keep your back straight, bend at the knees, and use your leg muscles.
If assistance is needed, request help from a colleague. Employ transfer aids like gait belts to provide a secure grip and control during the transfer. Lock bed brakes and ensure the environment is free of obstacles. Move slowly and deliberately, communicating throughout the process to maintain patient comfort and security.
Proper Body Mechanics for Nursing Assistants
Proper body mechanics are crucial for Nursing Assistants to prevent injuries while performing their duties. Always maintain a wide base of support with feet shoulder-width apart for stability. Bend at the knees, keeping your back straight, and avoid twisting your body. Hold objects close to your center of gravity to minimize strain.
When lifting, use your leg muscles, not your back. Anticipate the weight of the object and plan your movements. Avoid reaching or bending excessively. Utilize assistive devices when available, and request assistance when needed. Practicing these techniques consistently will safeguard your physical health and enable you to provide safe patient care.

Patient Care Essentials
Patient Care Essentials encompass nutrition, hydration, communication, and infection control, all vital for well-being and recovery, as outlined in Nurse Aide training.
Nutrition and Hydration
Providing adequate nutrition and hydration is a cornerstone of nursing assistant care. Assistants play a crucial role in assisting patients with meals, ensuring they receive the nourishment needed for recovery and maintaining health. This includes setting up trays, assisting with cutting food, and offering encouragement during mealtimes.
Monitoring fluid intake is equally important. Nursing assistants carefully observe and document how much fluid each patient consumes, reporting any concerns about decreased intake to the nursing staff. Proper hydration prevents dehydration and supports overall bodily functions. Understanding dietary restrictions and individual patient needs, as detailed in care plans and Nurse Aide training handbooks, is paramount for safe and effective care.
Assisting with Meals
As a nursing assistant, skillfully assisting with meals is vital for patient well-being. This involves more than simply delivering a tray; it requires understanding individual dietary needs and preferences, as outlined in the patient’s care plan and Nurse Aide training materials. Preparing the meal environment – ensuring a clean space and comfortable positioning – is crucial.
Providing assistance with cutting food, opening containers, and offering encouragement are key responsibilities. Observing for signs of difficulty swallowing or decreased appetite, and promptly reporting these to the nurse, is essential. Following proper food handling procedures and adhering to infection control protocols, detailed in handbooks, guarantees patient safety and a positive dining experience.
Monitoring Fluid Intake
Accurate monitoring of fluid intake is a fundamental nursing assistant duty, directly impacting patient hydration and overall health. This involves diligently recording the amount and type of fluids consumed by patients throughout the day, utilizing standardized measurement tools and documentation procedures as detailed in Nurse Aide training.
Observing for signs of dehydration – such as decreased urine output, dry mouth, or confusion – and promptly reporting these to the nurse is critical. Encouraging patients to drink regularly, offering preferred beverages, and assisting those with difficulty self-feeding are essential components of care. Adhering to specific fluid restrictions, outlined in the care plan and handbooks, is paramount for patients with certain medical conditions.
Communication and Interpersonal Skills
Effective communication forms the cornerstone of quality patient care, requiring nursing assistants to employ both verbal and non-verbal techniques. Active listening, maintaining eye contact, and using a clear, respectful tone are vital for building rapport and understanding patient needs, as emphasized in Nurse Aide training materials and handbooks.
Demonstrating empathy and compassion is equally crucial, acknowledging patients’ emotional states and providing reassurance. Adapting communication styles to accommodate individual cognitive abilities and cultural backgrounds ensures optimal understanding. Promptly reporting patient concerns and observations to the nursing staff facilitates timely intervention and contributes to a positive care environment, aligning with NATCEP standards.
Effective Communication Techniques
Mastering effective communication is paramount for nursing assistants, involving both verbal and non-verbal cues. Utilizing simple, clear language, avoiding medical jargon, and speaking slowly ensures patient comprehension. Active listening – paying attention, nodding, and summarizing – demonstrates respect and builds trust, as detailed in Nurse Aide handbooks.
Non-verbal communication, including maintaining eye contact and using a warm tone, reinforces verbal messages. Asking open-ended questions encourages patients to express their feelings and concerns. Reporting observations accurately and concisely to the nursing team is vital for coordinated care, adhering to NATCEP guidelines and promoting positive patient outcomes.
Empathy and Compassion in Patient Care
Empathy and compassion are cornerstones of quality nursing assistant care, requiring understanding a patient’s emotional state and responding with kindness. Recognizing that illness and hospitalization can cause fear and anxiety allows assistants to offer reassurance and support, as outlined in Nurse Aide training materials.
Showing genuine concern, actively listening to patient concerns, and providing a comforting presence can significantly improve their well-being. Respecting patient dignity, maintaining confidentiality, and treating each individual with respect are essential ethical considerations. These compassionate actions, detailed in candidate handbooks, foster trust and contribute to a positive healing environment.
Infection Control
Infection control is paramount in healthcare settings, and nursing assistants play a crucial role in preventing the spread of infections. Strict adherence to hand hygiene protocols – washing hands thoroughly and frequently – is the most effective method, as emphasized in Nurse Aide training programs and handbooks.
Standard precautions, treating all patients as potentially infectious, are essential. This includes using personal protective equipment (PPE) like gloves and gowns, proper handling of contaminated materials, and diligent cleaning and disinfection of surfaces. Understanding transmission-based precautions for specific infections, detailed in OBRA regulations and NATCEP standards, is also vital for patient and staff safety.

Hand Hygiene Protocols
Effective hand hygiene is the cornerstone of infection control, and nursing assistants must meticulously follow established protocols. This involves washing hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, covering all surfaces, and using a proper technique as outlined in Nurse Aide training handbooks.
Alcohol-based hand rubs are a convenient alternative when hands are not visibly soiled. The process requires applying enough product to cover all surfaces and rubbing until dry. Hand hygiene is crucial before and after patient contact, after removing gloves, and after touching contaminated surfaces. Consistent practice, reinforced by NATCEP standards, minimizes the risk of healthcare-associated infections.
Standard Precautions
Standard Precautions are a set of infection control practices used to minimize the risk of transmission of infectious agents from both recognized and unrecognized sources. Nursing assistants must consistently apply these precautions to all patients, regardless of their diagnosis, as detailed in Nurse Aide training materials and handbooks.
Key elements include hand hygiene, use of personal protective equipment (PPE) like gloves, gowns, and masks, and safe handling of contaminated items. Proper disposal of sharps and adherence to respiratory hygiene/cough etiquette are also vital. NATCEP standards emphasize that consistent application of Standard Precautions protects both the patient and the healthcare worker.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Nurse Aides must uphold patient rights, maintain confidentiality, and promptly report any suspected abuse or neglect, per OBRA regulations and handbooks.
Patient Rights and Confidentiality
Nursing Assistants play a crucial role in safeguarding patient rights, ensuring dignity and respect in all interactions. These rights encompass informed consent, the right to refuse treatment, and privacy regarding personal and medical information. Maintaining confidentiality is paramount; Nurse Aides must never disclose patient details to unauthorized individuals, adhering strictly to HIPAA guidelines and facility policies.
Detailed information regarding these rights is often outlined in Nurse Aide Candidate Handbooks and during training programs. Understanding and upholding these ethical and legal obligations builds trust and fosters a safe, supportive environment for those receiving care. Protecting patient information is not merely a legal requirement, but a fundamental aspect of compassionate and ethical healthcare practice.
Reporting Abuse and Neglect
Nursing Assistants are mandated reporters, legally obligated to immediately report any suspected instance of patient abuse, neglect, or exploitation. This duty extends to witnessing or even suspecting harm inflicted by anyone, including colleagues or family members. Recognizing the different forms of abuse – physical, emotional, sexual, financial – is crucial, as is understanding the signs of neglect.
Nurse Aide training, and resources like the Nurse Aide Candidate Handbook, provide detailed guidance on reporting procedures. Facilities typically have specific protocols to follow, ensuring prompt investigation and protection for vulnerable individuals. Failure to report can result in legal penalties. Prioritizing patient safety and well-being demands vigilance and a commitment to ethical conduct.

Resources and Training
NATCEP standards and the Nurse Aide Registry offer crucial information, while the Nurse Aide Candidate Handbook guides aspiring professionals through certification.
Nurse Aide Registry Information
Nurse Aide Registries are state-specific resources vital for verifying the credentials and employment eligibility of certified nursing assistants. These registries maintain comprehensive lists of individuals who have successfully completed a state-approved training program and passed the competency evaluation.
Information typically found within a Nurse Aide Registry includes the aide’s name, certification number, date of certification, and any disciplinary actions taken against them. Employers utilize these registries to ensure they are hiring qualified and trustworthy personnel to provide patient care.
Accessing registry information is often available online, allowing for convenient verification. Minnesota, for example, has a publicly accessible registry, emphasizing transparency and accountability within the healthcare system. Maintaining an active listing on the registry is crucial for continued employment as a certified nursing assistant.
NATCEP Standards (Nurse Aide Training and Competency Evaluation Program)
The Nurse Aide Training and Competency Evaluation Program (NATCEP) establishes standardized guidelines for training and evaluating prospective nursing assistants. As defined by OBRA regulations, NATCEP ensures consistent quality across training programs nationwide. These standards dictate the minimum curriculum hours, required clinical skills, and the format of the competency exam.
NATCEP-approved programs must cover essential topics like basic nursing skills, patient rights, infection control, and communication techniques; The competency evaluation typically consists of a written exam and a skills demonstration, assessing the candidate’s ability to perform tasks safely and effectively.
Adherence to NATCEP standards is crucial for program accreditation and for ensuring that graduates are well-prepared to provide high-quality patient care. These standards promote competency and safeguard patient well-being.
Nurse Aide Candidate Handbook
The Nurse Aide Candidate Handbook serves as a vital resource for individuals preparing for certification. It details the entire certification process, including eligibility requirements, application procedures, and exam information. These handbooks, like the Minnesota version, often outline the curriculum covered in approved training programs, ensuring candidates understand the expected competencies.

Key sections typically include information on the written and skills evaluations, test-taking strategies, and what to expect on exam day. The handbook also clarifies candidate rights and responsibilities, as well as procedures for appealing exam results.
Reviewing the handbook thoroughly before the exam is strongly recommended to maximize preparedness and reduce anxiety, ultimately leading to successful certification.

